When practicing yoga, we often hear a word called “super stretch”.

For example, yoga teachers often remind us: tighten the thigh muscles to prevent knee hyperextension, slightly rotate the elbows, keep the elbows eye to eye, avoid elbow hyperextension, and so on.

There are often Jia people who leave messages to Xiaobian.
What about super extension? Is overstretch a big influence? But we do not know what is wrong or harmful.
It’s better to be right than to practice more.

To solve the problem of overstretch, let’s analyze what overstretch is? What are the hazards? How? How to test whether you overstretch? How to correct? Through this knowledge, people can correct their own problems.
Yoga teachers can give members guidance on Theory + practice.

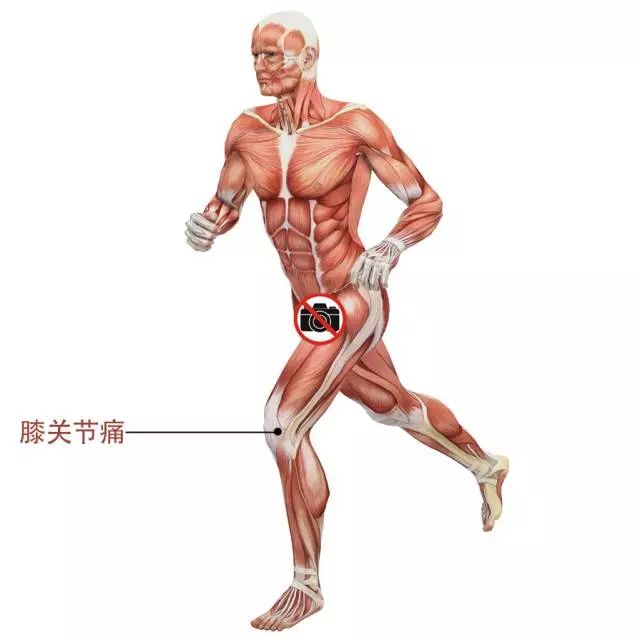
What is “elbow / knee” hyperextension? In fact, from the literal meaning, we can simply understand that the extension angle of the knee / elbow exceeds its original physiological curvature.
For example, when a person straightens his arm and stretches his elbow joint, his arm usually looks like a straight line, that is, a flat 180 º.
So the so-called elbow hyperextension means that when the arm is flat, the opening angle exceeds 180 º.
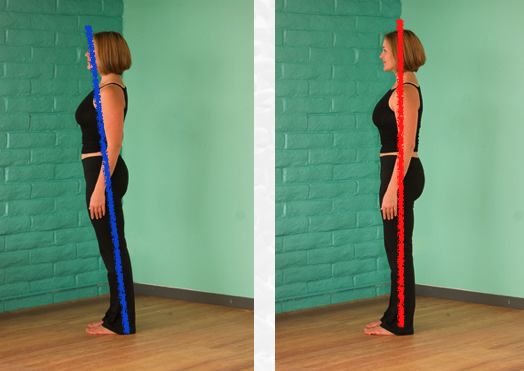
As shown in the above figure, the pelvis, knee and ankle are basically in a straight line when the human body is standing.
However, if the knee is further extended backward for more than 15 degrees, and the thigh and calf form an arc similar to “C”, the knee extension is formed, which is also called knee reverse bow.
Causes of “elbow / knee” hyperextension 1 Congenital factors family inheritance, ligament relaxation, excessive activity 2 Acquired factors 1) injury caused by external force 2) particularity of Sports 3) poor body posture 4) abnormal gait (such as gluteal myasthenia, supporting the knee joint to be excessively stretched) what is the harm of “elbow / knee” hyperextension? The danger of elbow hyperextension is slightly smaller, because modern people do not walk with their hands, which is easier to be ignored.
Hyperextension of the elbow can cause elbow arthritis (tennis elbow).
Let’s first understand the structure of the lower elbow joint.
The structure of normal elbow joint the elbow joint is composed of three bones: humerus, ulna and radius.
The connection between the ulna and humerus (the connection between the humeral trochlear and the olecranon of the ulna) plays an important role.
Elbow hyperextension will cause constant friction between the olecranon of the ulna and the humeral trochlear, resulting in joint damage and inflammation.
Therefore, hyperextension is actually caused by the fact that the muscles at the front and rear sides of the joint are too loose, and the front and rear space is inconsistent when stressed, which does not play a role in fixing the legs or arms.
Its specific harm is caused by repeated and long-term practice of hyperextension in yoga.
It will cause cartilage wear, resulting in pain or muscle spasm, weakening joint vitality, and may also produce a state of numbness.
02 hazards of knee joint hyperextension? 1.
cause knee pain.
The kneecap will be too close to the femur during rest or movement, resulting in excessive friction.
If it takes a long time, it will cause knee pain.
2.
Unable to complete some actions, knee hyperextension posture cannot complete some high impact actions, such as jumping, fast running, etc., which will increase the risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury.
3.
It will make the calf thicker and the gastrocnemius muscle grows on the calf, but it is connected with the thigh.
When the knee joint is over extended, the knee joint will be backward, making the upper and lower ends of the gastrocnemius muscle longer.
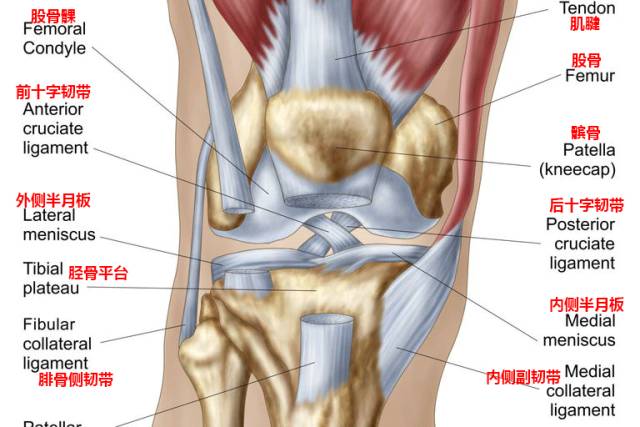
Let’s first understand the structure of the lower knee joint.
The structure of normal knee joint the knee joint is a hinge joint formed by femur and tibia, which is held together by four ligaments (medial collateral ligament, lateral collateral ligament, anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament).
When the knee joint is not overstretched, the strength of the upper body will be well distributed to the legs, and then flow to the earth.
The ground will transmit a reaction force to the legs, so that people can stand firm and walk straight…
When the knee joint is overstretched, the pressure cannot be well dispersed, but is concentrated on the knee joint, so the knee will feel pain from time to time, and even cause strain.
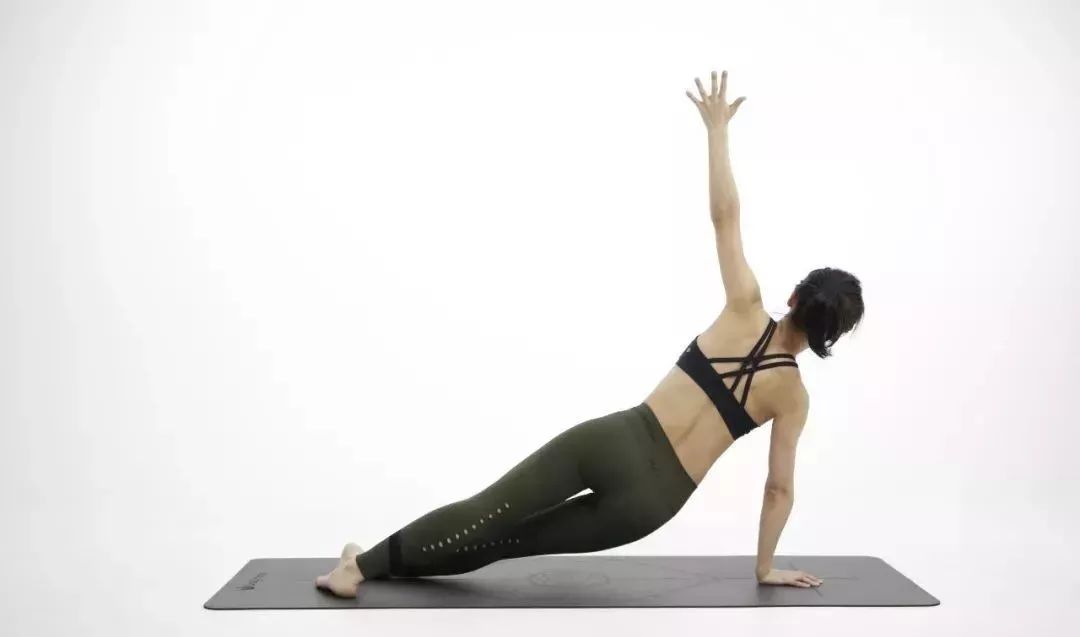
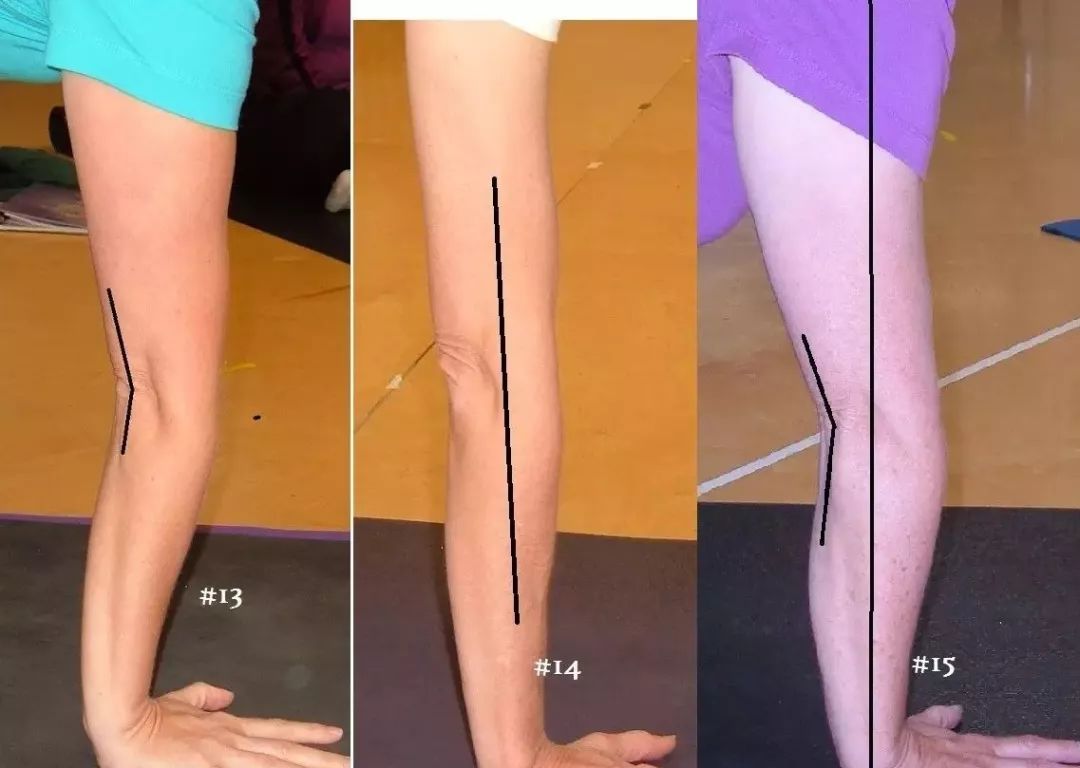
How to test whether the “elbow / knee” is over extended? We use the side plank pose to visually see what the elbow hyperextension looks like in the yoga pose.
Positive position 1.
Support the ground with your right hand and point your feet back and forth.
Hold your body up so that your head and neck are in line.
2.
keep your right arm straight without shrugging.
Elbow hyperextension: 1 Elbow hyperextension serious 2 Shrug your shoulders and collapse your body.
How to avoid “elbow / knee” overstretching? 1.
In yoga, to avoid elbow hyperextension, there are the following main points: shoulder joint is in the right position, the straight arm makes efforts to avoid locking the elbow joint as much as possible, the arm is slightly rotated inward to find the feeling that the upper humerus sinks to the shoulder socket, and the force of arm internal rotation is used to neutralize the hyperextension caused by external rotation.
Bend the elbow slightly, and the elbow eye is opposite to avoid hyperextension.
2.
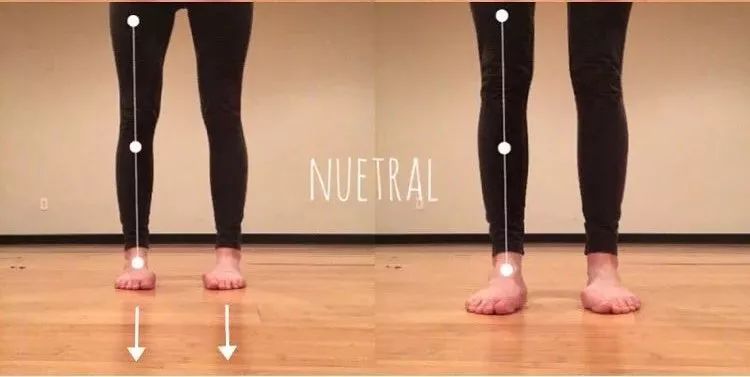
In yoga, to avoid knee hyperextension, there are the following main points: insert the femoral head into the hip joint in the right position to maintain the hip The knee and toe are in a straight line, the thigh muscles are tightened, the patella is lifted up to balance the body strength, do not focus too much pressure on the knee and slightly bend the knee, and avoid the correction method of “elbow / knee” hyperextension 01 hyperextension of the elbow joint to improve the hyperextension of the elbow joint, it is necessary to strengthen the strength of the elbow flexors (mainly the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, biceps brachii, brachioradialis brachii and brachialis muscle) To relieve elbow hyperextension, you can do more exercises of biceps brachii contraction, which should emphasize muscle tightening.
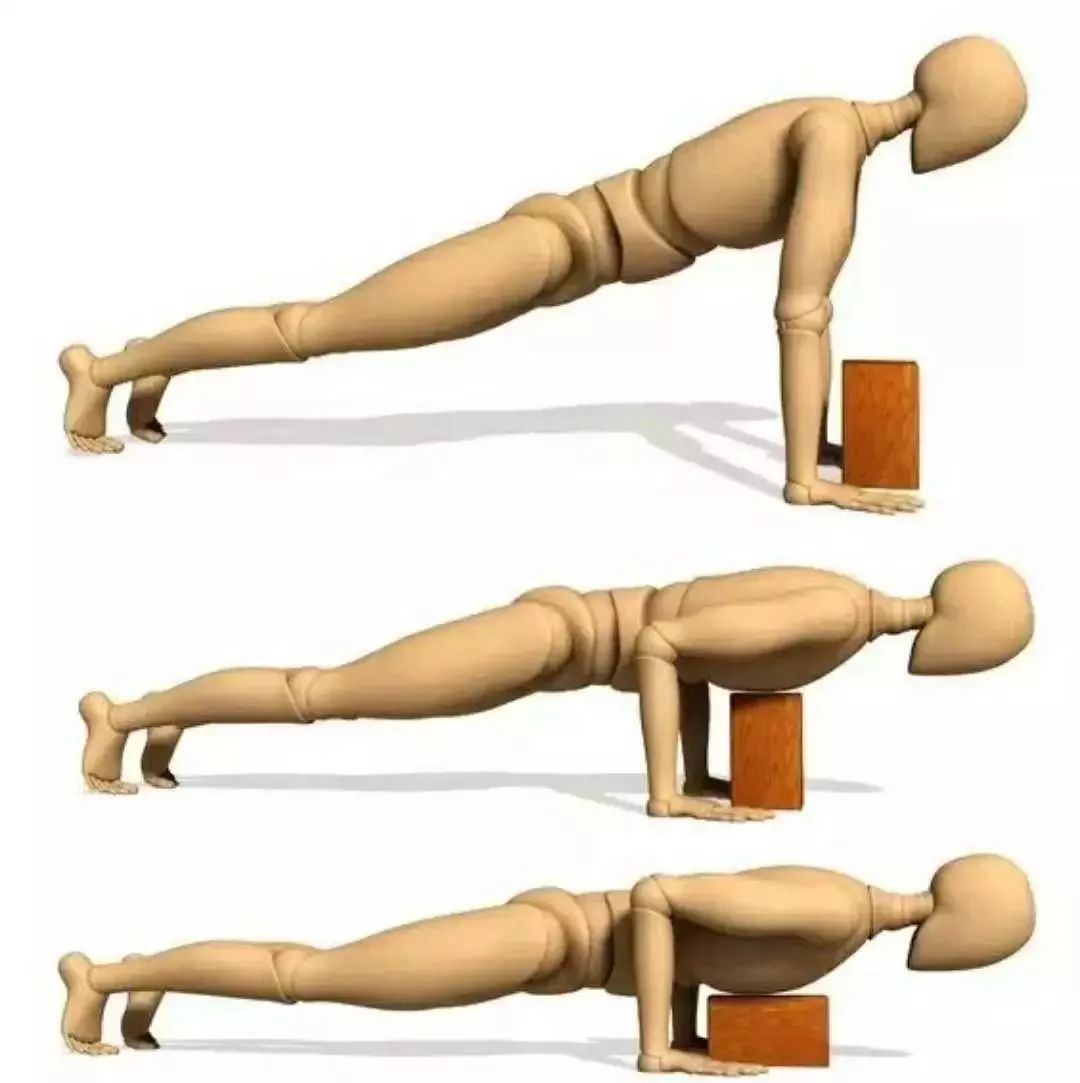
Eight limb pose, back extension pose and four column pose are all good exercises.
Key points of the four column pose: start from the inclined plank, keep your body in a straight line from head to foot, don’t step on your waist and hips, tighten the core part, keep the posture of the inclined plank unchanged, slowly bend your elbows downward, make your big and small arms 90 degrees, and clamp your chest with your big arm parallel to the ground to enter the four column pose.
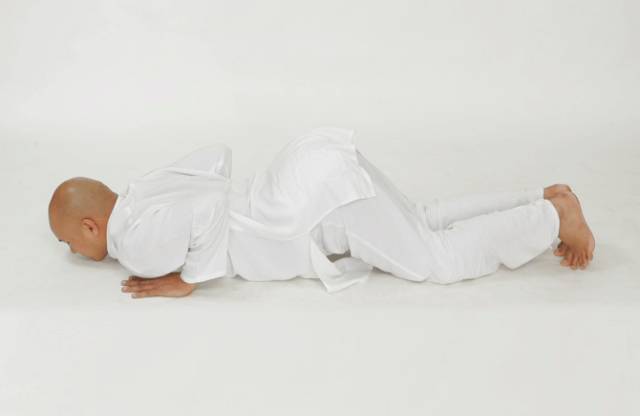
Key points of the eight limb pose: place the knee on the mat.
When exhaling, roll the tailbone upward, bend the elbow backward and downward, clamp the ribs with the arm, and let the chest and chin fall directly on the mat.
When out of the pose, breathe and put the body flat on the mat..

