▲ xzlyoga focuses on the application of Yoga health physiotherapy to make your exercise correct! Safe! Efficient! According to statistics, when people walk, the pressure on their feet is 1.2 times our weight; If you jump, you have to bear the pressure up to 5 times your weight.

In other words, if a person weighs 60 kg and walks 8000 steps a day, his feet will have to bear a ground reaction force of up to 576 metric tons.
A pair of small feet less than 5kg have to bear such a great force.
If our foot structure is normal and the muscle system consumes the least force, it can also support the weight of the body and help us save “physical strength”.

If it is not normal, it will cause various problems.

Therefore, foot awareness is very important in yoga practice and even in daily life.

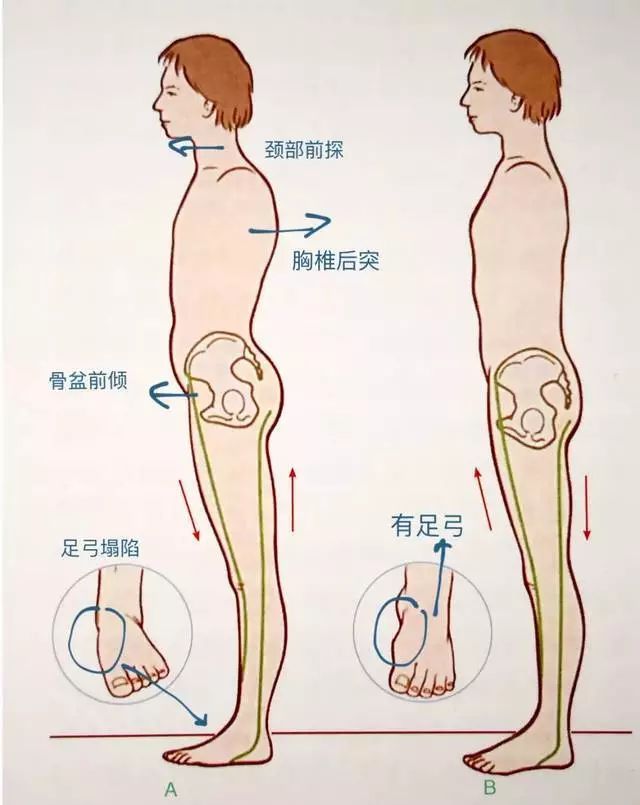
“Natural shock absorber” – if the foot arch is a building, the sole of the foot is the foundation.

If the sole of the foot is bad, the whole body falls down.
The most important thing to exercise the soles of the feet is to exercise the arch of the foot! When doing yoga standing three-dimensional, the teacher will say “both feet are rooted and the arch of the foot is raised”.
So you must know what the arch looks like first? What does it do? And how does the foot arch come into being? The structure of the foot arch the foot arch is a bone arch composed of many unique shaped bone blocks with wide upper and narrow lower.
If it is normal and stable, once it is loaded, it will be appropriately reduced to transmit gravity to the ligament.
When the ligament reaches appropriate tension, the internal and external muscles of the foot will begin to contract to assist the ligament to maintain the structure of the foot arch.
1.
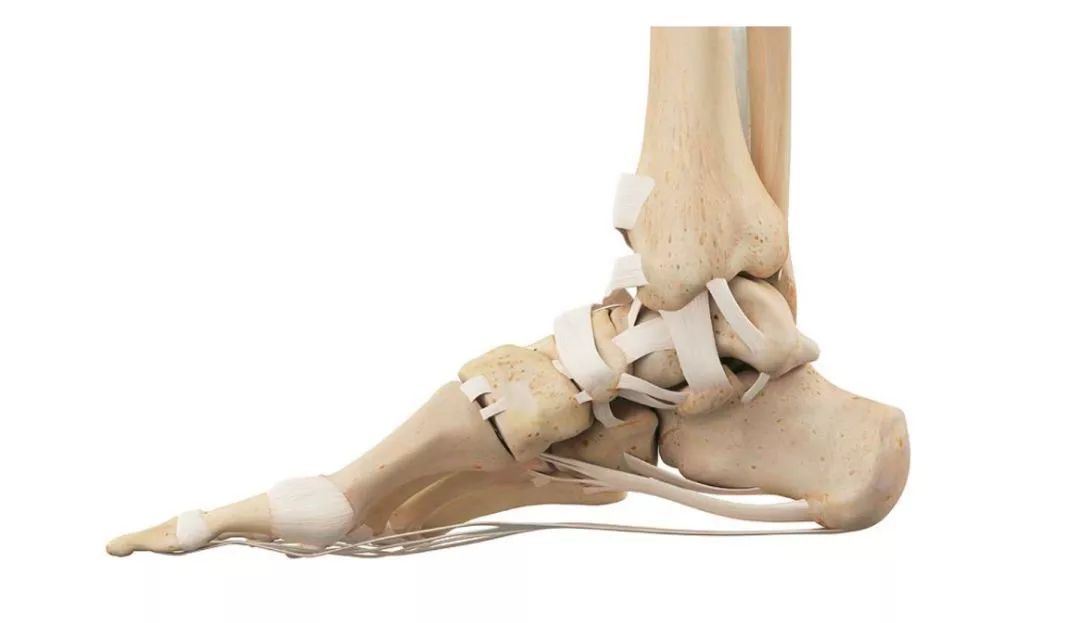
> > > foot bones < < there are 26 foot bones and 36 joints.
The center of gravity of plantar distribution has two important landing points: one is the heel, accounting for about 50%, the other is about 1 / 3 of the front of the foot, and the junction of metatarsal and phalangeal bones, accounting for about 25%.
Except for sesamoid bone and talus bone, both have a wide back and a narrow bottom.
When they are combined, they naturally form an arched structure.
2.
> > > ligament < < ligament is an important tissue to maintain the connection between the bone blocks of the arch of the foot.
The dorsum of the foot is prominent, the load is less, the ligament is weak, and the plantar side load is large.
It is also particularly important for the maintenance of the arch of the foot, so the ligament is thick and strong.
The tibiocalcaneal ligament of the medial triangular ligament of the ankle connects the medial malleolus and calcaneus to prevent its valgus.
3.
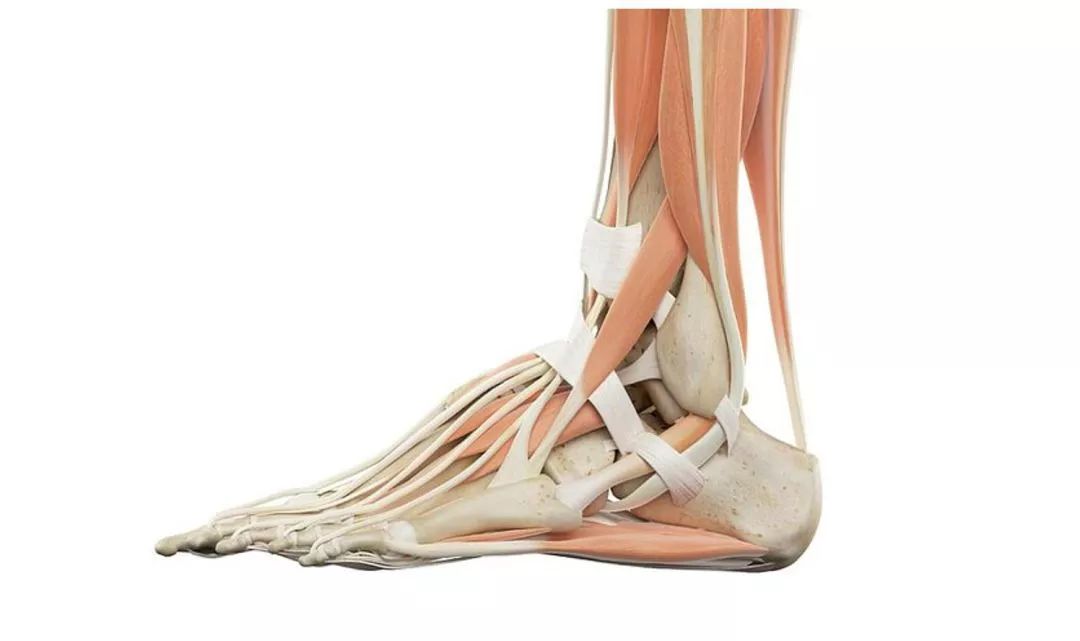
> > > muscle < < muscle is the main line of defense to maintain the arch of the foot.
The foot muscles are divided into internal muscles and external muscles.
The former degenerates, has little effect on the human body, and only plays an auxiliary role in the maintenance of the foot arch.
The value of activating the foot arch the foot arch is a convex upward arch structure composed of the tarsal bone, metatarsal ligament and tendon of the foot.
It can be divided into medial longitudinal arch in front and back direction, lateral longitudinal arch and transverse foot arch in inside and outside direction.
The medial longitudinal arch, also known as the elastic arch of the foot, plays a role in cushioning shock.
The lateral longitudinal arch is mainly related to maintaining the upright posture of the body, also known as the supporting arch.
The arch of the foot is in an arched structure, which makes the foot strong, lightweight and elastic.
It can withstand large pressure and buffer the vibration to the body when walking, running and jumping.
At the same time, it can also protect the blood vessels and nerves under the foot from compression.
From a to B, this is called the medial arch, which belongs to the elastic foot arch.
From a to C, this is called the lateral arch, which belongs to the supporting arch of the foot.
The one from B to C is called the transverse arch, which belongs to the balanced arch of the foot.
When the teacher says “press the ground down with both feet”, he means to make the three ABC points more compact.
When he says “lift the foot arch”, he means to lift the connection of these three points.
This method is very similar to the state of the suction cup when we want to pull it out of the plane.
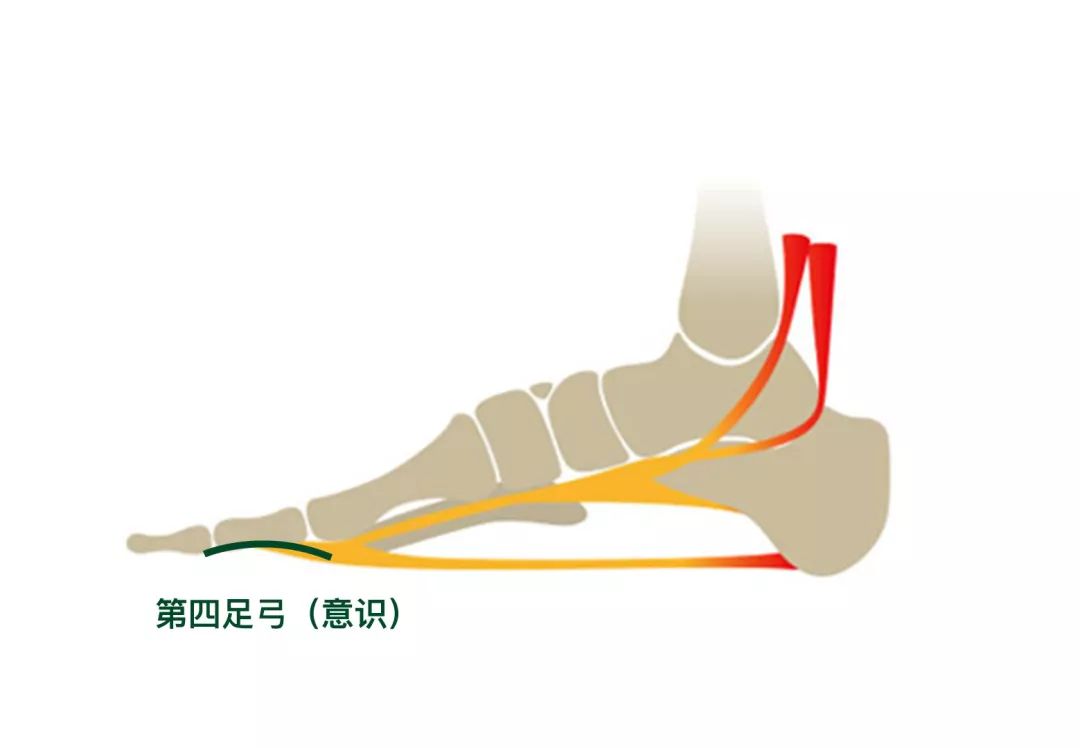
In traditional Indian yoga, there is a fourth arch.
In charge of consciousness.
(the horizontal bow is in charge of breathing, and the lateral bow is in charge of the body).
The foot arch also has a significant impact on the energy state of the human body.
People with foot arch are alert.
People without foot arch are more likely to be lazy and drowsy.
If they are flat feet, their fatigue degree or fatigue rate are higher.
How does the foot affect other parts of the body? The foot arch also has a significant impact on the energy state of the human body.
People with foot arch are alert.
People without foot arch are more likely to be lazy and drowsy, that is to say, the fatigue degree or fatigue rate are higher.
If there is a problem with the foot mechanism and affects the gait, the center of gravity of the body will change to an incorrect position.
So the pressure on the soles of the feet, pelvis and spine will be unbalanced.
For a long time, in addition to plantar fasciitis, hallux valgus, bone spur and degeneration, it will also cause pelvic distortion, lower back pain, scoliosis and other diseases (long-term waist pain, chest tightness, shoulder and neck pain, etc.).
Therefore, the effect of foot arch on human body can always be from foot to head.
The soles of your feet are like the “foundation” of your body.
There are some answers to the problems caused by your legs, pelvis and spine.
If you have some physical problems such as pelvic, lumbar, thoracic and cervical problems, it’s better to check the foot arch first.
How to judge whether your arch is normal? Too low or too high arch will have a bad impact on the overall posture of the body.
Helping the arch adjust to the normal radian is the basis for us to improve the state of the sole.
So how do you judge whether you have a normal arch? 1.
First prepare a basin of lime and a blackboard, then step barefoot in the lime to ensure that all soles of your feet are stained with lime, and then step on the blackboard to observe the footprints on the blackboard.
2.
If most of the footprints on the blackboard are obvious, and only the middle and outer parts are not obvious, it is proved to be a normal arch; If the footprints seen are complete and there is no gap in the middle, they belong to flat feet; If the footprints seen are only the traces of the sole and heel of the foot, and there are almost no traces of the belly of the foot, it is a high foot arch.
1.
Recognize that flatfoot can be divided into flexible flatfoot and rigid flatfoot.
Plastic flatfoot means that when standing, the load of weight makes the arch collapse or disappear, while when there is no weight load, the arch is normal.
This type of flatfoot is mainly caused by the thick fat on the sole of the foot and the weak strength of muscles and tendons.
For this type of flat foot, strengthening ankle and calf muscle training can compensate for arch collapse, and the correction effect is good.
The arch of rigid flat foot collapses or disappears when it is loaded or not.
This type of flat foot is often caused by the deformity of the mutual position of the bones forming the arch of the foot.
This condition is difficult to correct and the effect of surgical treatment is better.
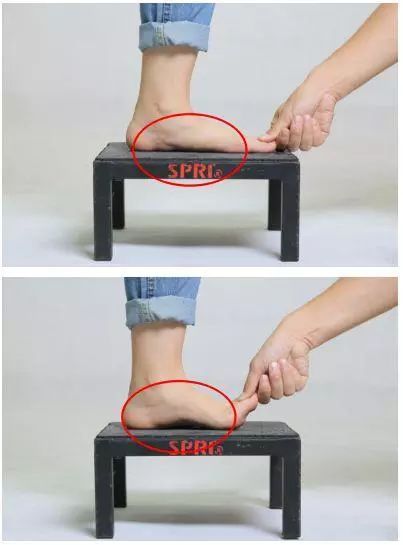
If you have flat feet, raise your thumb.
If the arch of the foot is restored, it means that it is plastic and flat, and there is more room for correction.
If the arch of the foot cannot be restored after the thumb is raised, it indicates that it is a rigid flat foot.
2 recognize that high arch foot is opposite to flat foot.
High arch refers to abnormal high internal arch.
High arches usually cause uneven force distribution when the foot is under pressure.
The soles of the feet are arched, like eagle claws.
In this way, more pressure on the foot falls on the outside of the sole when walking, and the shock absorption effect is small, which makes the external ankle and knee feel pain.
In severe cases, it will lead to external rotation of the hip joint and retroversion of the pelvis.
How to activate the foot arch in yoga practice? In fact, our seemingly simple foot arch has a great impact on the body.
Therefore, protecting the foot, reactivating the foot muscles and improving the awareness of both feet can help the body return to the political commissar and bring significant changes to the body..